The Science of Climate Change: What We Know and What We Can Do.

Explore the scientific consensus on climate change, its causes, impacts, and actionable solutions. Learn how human activities contribute to global warming and discover strategies to mitigate its effects.
Understanding Climate Change.
Climate change represents one of the most pressing challenges of our time. Scientific research has unequivocally shown that human activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases, are driving unprecedented changes in our planet's climate system. Understanding the science behind climate change is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its impacts and adapt to new environmental realities.
The Scientific Consensus on Climate Change.
The global scientific community agrees that:
- Earth's Climate Is Warming: Data from NASA indicates that Earth's average surface temperature has risen significantly since the late 19th century, largely due to increased carbon dioxide and other human-made emissions.
- Human Activities Are the Primary Cause: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) states with high confidence that human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, are the dominant cause of observed warming since the mid-20th century.
- Consequences Are Far-Reaching: Climate change leads to rising sea levels, more extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems and biodiversity.
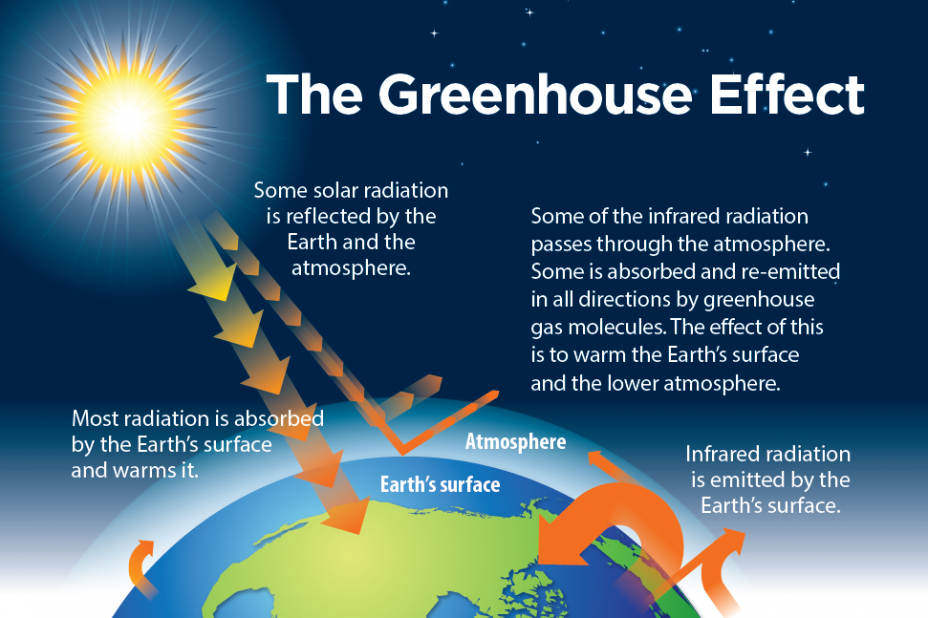
Key Indicators of Climate Change.
1. Rising Global Temperatures
Global surface temperatures have increased, with recent years being the warmest on record. This trend correlates strongly with the rise in greenhouse gas concentrations.
2. Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels
The loss of ice from glaciers and polar ice sheets contributes to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities worldwide.
3. Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is linked to more frequent and severe weather events, including hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, impacting ecosystems and human societies.
What We Can Do: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies.
1. Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Global surface temperatures have increased, with recent years being the warmest on record. This trend correlates strongly with the rise in greenhouse gas concentrations.
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Adopting solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Enhance Energy Efficiency: Improving insulation, using energy-efficient appliances, and adopting smart technologies can lower energy consumption.
- Promote Sustainable Transportation: Encouraging public transport, cycling, and electric vehicles reduces emissions from the transportation sector.
2. Implement Climate-Smart Agriculture
Practices such as crop diversification, conservation tillage, and efficient water use enhance resilience to climate impacts and reduce emissions.
3. Protect and Restore Ecosystems
Conserving forests, wetlands, and other natural habitats sequesters carbon and supports biodiversity.
4. Support Climate Policy and Education
Advocating for policies that address climate change and educating communities about sustainable practices are vital for collective action.
Addressing climate change requires a concerted effort from individuals, communities, businesses, and governments. By understanding the science and implementing practical solutions, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and build a more sustainable and resilient future for all.




